Eponymous fractures of Lower limb
EPONYMOUS
FRACTURES (LOWER LIMB)
LOWER LIMB FRACTURES
Jefferson Fracture-
It generally occurs at C1 vertebra; it occurs by compression
of neck.
Hangman’s Fracture-
In this both pedicles of C2
over C3 fractures; mainly occurs due to distraction and extension of
neck.
Clay-Shoveler’s Fracture-
It’s a stable fracture and involves lower spine of cervical
and upper thoracic ( C6 or C7). Its an
injury of spinous process of lower cervical spine.
Chance Fracture-
It’s a very common fracture which occurs due to hyperflexion
of spine (seen in car accidents). There is compression injury to anterior
portion of vertebral body.
Duverney’s Fracture-
It’s a pelvic fracture involving iliac wings. This fracture
doesn’t interfere with the main pelvic ring.
Malgaigne’s Fracture-
Its also referred as Supra-condylar fracture of humerus. In
this sacro-iliac joint along with pubic rami gets injured, compressing the
pelvis front to back.
Straddle Fracture-
It’s a bilateral fracture of superior and inferior pubic
rami; mode of injury is fall from a height or motorcycle accident.
Pipkin’s Fracture-
It impacts the knee when the hip is flexed. In this there is
posterior dislocation of hip with avulsion fracture of fragment of femoral head
by teres ligament. This fracture is divided into –
1.
Type I – fracture of head inferior to the fovea
2.
Type II – segment of the head superior to the
fovea
3.
Type III – head with neck fracture
4.
Type IV – fracture of head along with fracture
of acetabulum with dislocation.
Bumper Fracture-
Fracture of lateral tibial plateau due to valgus injury of
the knee. This fracture occurs due to forced valgus of the knee when it has
been struck from side by car’s bumper.
Pott’s Fracture-
We have 3 malleoli at the ankle – medial (by tibia),
Lateral(by fibula) and Posterior(by lower part of the tibia); Pott’s fracture
is fracture of the 2 malleoli (injury to medial and lateral malleolus). Mode of
injury is eversion of the ankle.
Cotton’s Fracture-
It’s a trimalleolar fracture.
Dupuytren Fracture-
It’s a specific Bimalleolar fracture. In this the fracture
of distal portion of fibula above the lateral malleolus along with tear of
tibio-fibular ligament & deltoid ligament occurs, leading to lateral
displacement of talus, finally causing fracture of the Medial malleolus.
*Deltoid ligament is a structure that if it is damaged,
causes swelling without an X-ray change.
Gosselin Fracture-
It’s a type of lower tibial injury. It’s a “V-shaped”
fracture of lower tibia going till the ankle joint but there’s split in
anterior posterior fragment in coronal plane.
Tillaux- Chaput
Avulsion Fracture-
Its Salter-Harris type III injury; occurs due to pull of
Tibio-fibular ligament. The mode of injury is forced lateral rotation of the
foot.
Le-Fort’s Fracture
Of Ankle-
It occurs when fibular part breaks and the tibial is intact.
It is just the opposite of Tillaux-Chaput avulsion fracture.
Lisfranc Fracture-
Its an injury of the foot in which one or more than one metatarsal
bones are displaced from tarsus (involves Tarso-Metatarsal joint). The mode of
injury is forced plantar flexion of foot or dropping heavy weight on foot.
Chopart’s Fracture-
In this there is dislocation of mid-tarsal joint
(Talo-navicular and Calcaneo-cuboidal) along with fracture of calcaneous,
cuboid & navicular bones. Thus, this involves Inter-tarsal joint.
Jone’s Fracture-
It occurs due to inversion of ankle. In this meta-diaphyseal
junction of 5th meta-tarsal of foot.
Pseudo-Jone’s Fracture-
In this there’s avulsion fracture of the tip. Its proximal
to Jone’s fracture.
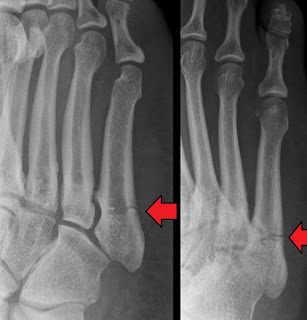
March Fracture-
Mode of injury is heavy or unaccustomed exercise. In this
there’s fracture of distal 3rd of one of the metatarsals; occurs due
to recurrent stress.
Runner’s Fracture-
It involves lower part of fibula. The mode of injury is due
to repeated axial stress on fibula. It’s a stress fracture of distal fibula
(3-8cm) above the lateral malleolus.
Segond Fracture-
It occurs due to avulsion injury (internal rotation of the
knee). It involves lateral tibial condyle along with soft tissue structure.
This small fragment is mostly associated with injury of Anterior cruciate
ligament.
Shepherd’s Fracture-
It’s a fracture of lateral part of posterior process of
talus.
Stieda Fracture-
It occurs due to avulsion fracture of medial femoral condyle
at the origin of the medial collateral ligament.
Toddler’s Fracture-
It involves lower part of tibia; generally its missed. Its
spiral injury. The mode of injury is low energy trauma , often rotation. Mostly
seen in 9months-3years & <8 years
of children.




























Comments
Post a Comment